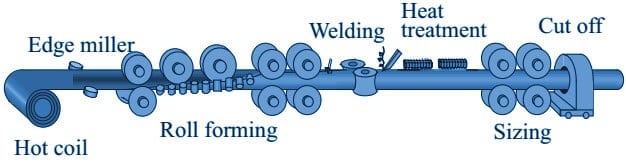
welded pipes are manufactured from plate or continues coil or strips. to manufacture a welded pipe, the first plate or coil is rolled in the circular section with the help of a plate bending machine or by a roller in the case of a continues process.
once the circular section is rolled from the plate, the pipe can be welded with or without filler material. a welded pipe can be manufactured in large sizes without any upper restriction. welded pipe with filler material can be used in the manufacturing of long radius bends and elbow.
there are different welding methods used to weld the pipe.
erw- electric resistance welding
efw- electric fusion welding
hfw- high-frequency welding
saw- submerged arc welding (long seam & spiral seam)
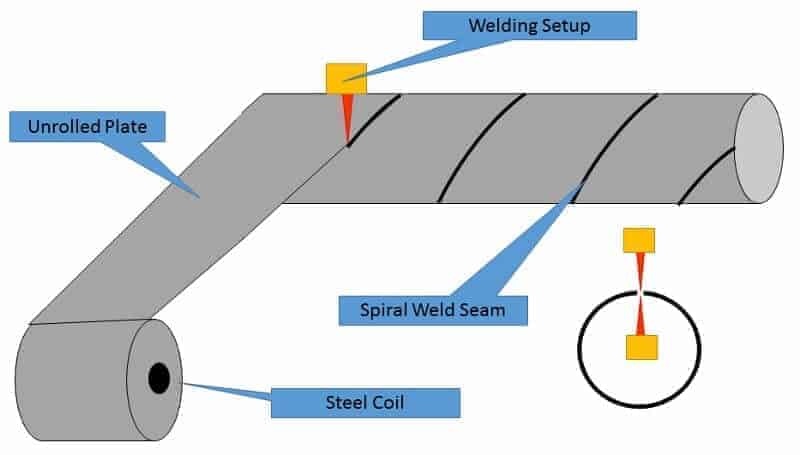
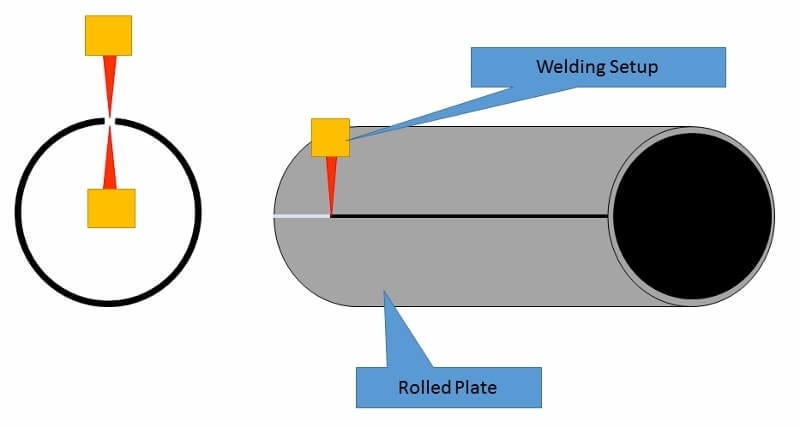
api 5l or astm welded steel pipe includes lsaw pipe, ssaw pipe, and erw steel pipe.
welded pipe advantages:
cost: a big advantage of welded pipe is that it is the least expensive of all pipe types and it is much more readily available.
consistency: it is generally accepted that the wall thickness of welded pipes is much more consistent than that of seamless pipes. this is because the manufacturing process starts with a flat sheet of steel.
surface quality: the avoidance of the extrusion process also means that the surface of a welded pipe can be much smoother than a seamless pipe as well.
speed: shorter procurement lead time is required for welded pipe due to the manufacturing process being simpler.
we provide welded steel pipe as standard:
astm a53 pipe, steel, black and hot-dipped, zinc-coated, welded
astm a135 electric-resistance-welded steel pipe
astm a795 black and hot-dipped zinc-coated (galvanized) welded steel pipe
bs 1387 black and hot-dipped zinc-coated (galvanized) welded steel pipe
en 10255 non-alloy steel tubes suitable for welding and threading
jis g3444 carbon steel tubes for general structural purposes
